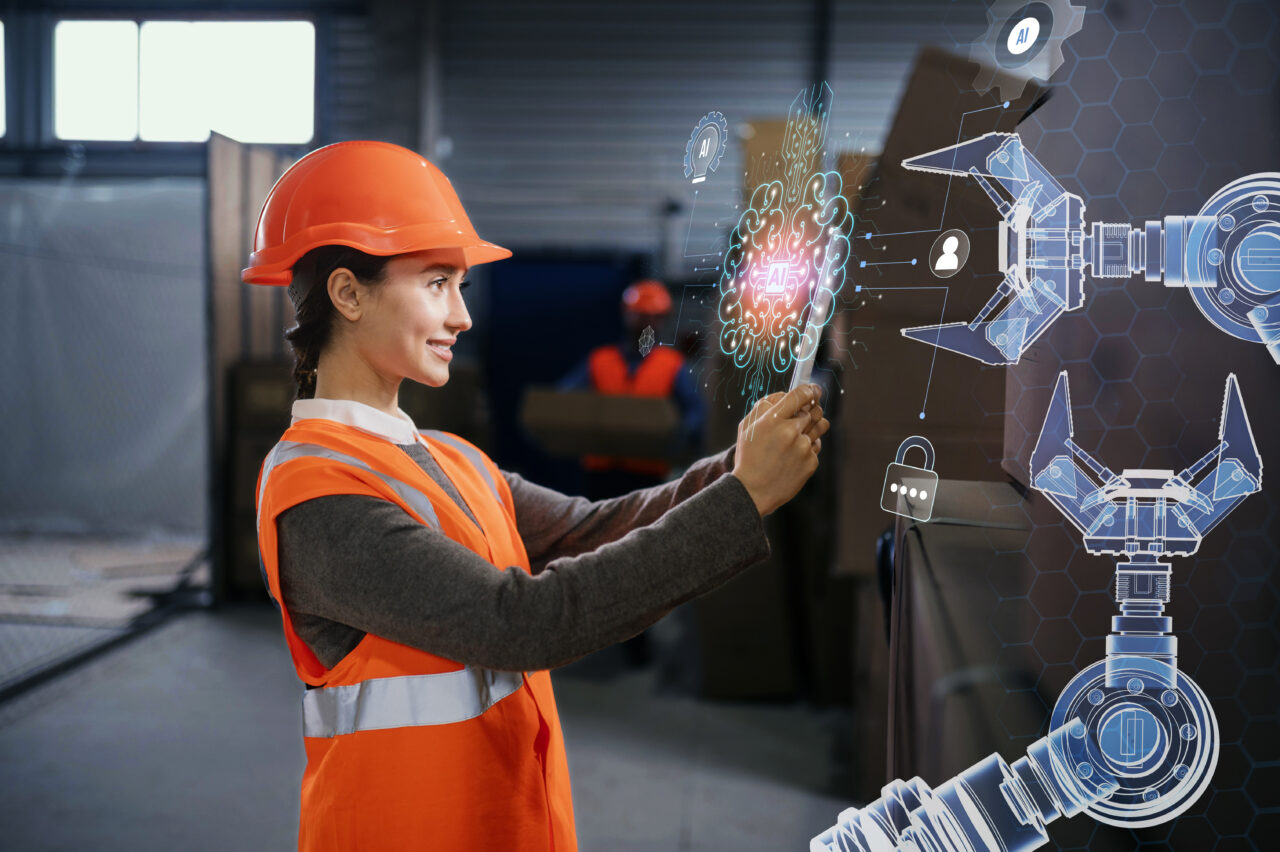
The processes of modernization and digitalization in industry production mark a paradigm shift in a world increasingly focused on customer-centric production rather than product-focused approaches.
Beyond meeting specific needs, industrial processes now leverage data to gain a clearer understanding of where, when, and how their products are consumed.
These changes are rooted in what is currently known as Industry 4.0, the so-called fourth industrial revolution according to experts.
The advent of Industry 4.0 has enabled changes and new operational methods for companies across various sectors that were previously unimaginable.
But what exactly has changed? What technologies are enabling Industry 4.0 to become an inevitable movement for industries and other organizations worldwide?
To learn more about Industry 4.0 and its key technologies and impacts, follow the content below.
What is Industry 4.0?
Also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0 is part of a sequence of revolutions that began in the 18th century and have affected industrial production processes.
These revolutions have brought about a series of crucial changes in how industries operate. Moreover, they have brought unprecedented transformations to production and consumption relationships.
Since then, new technologies have emerged, altering how industries manufacture goods and interact with their partners, as well as how products are received by consumers.
For instance, industries have recognized the importance of efficiently building and managing supply chains to streamline production and procedures.
This process has enabled stakeholders in the production chain to build integrated relationships, thereby generating more value for the end consumer. Consequently, it has fostered stronger partnerships as a competitive factor in the market.
But what sets Industry 4.0 apart from the other major revolutions in the industrial sector?
Essentially, Industry 4.0 adds a new layer to automated production procedures: the digitization of processes and the data involved in this digitization.
We know that advancements in information technology and the proliferation of big data have driven companies across all sectors into a process of digital transformation.
This means that methods within a company undergo a transformation aimed at optimizing and adapting them to the digital reality present in the contemporary world.
For industries, this initially meant automating their tools and increasingly focusing production on the consumer.
Industry 4.0 and the transformation of processes
It's important to remember that Industry 4.0 goes beyond deploying autonomous machines in production; it involves transforming and digitizing production processes based on various data sources.
This modification and the advent of these new technologies have also brought the challenge of managing the vast amount of data these tools and means produce. Consequently, data intelligence has become crucial in this new scenario.
The sheer volume of data requires precise interpretation to transform it into relevant information that can ultimately support industry decisions.
This relationship between data and information alters how an industry operates and, consequently, its relationship with consumers and clients.
This transformation in relationships is only possible because these technologies enable the integration of diverse data sets, thereby facilitating the creation of more accurate diagnostics and scenarios for these companies.
Advent of Industry 4.0
When it comes to the transformations brought by Industry 4.0, the technologies inherent in the concept also take center stage, as they play a crucial role in the process.
Whether it's the focus on data, the key characteristics of the tools, or even the philosophy guiding a particular operation, some advancements are intrinsic to Industry 4.0. Examples of these advancements include:
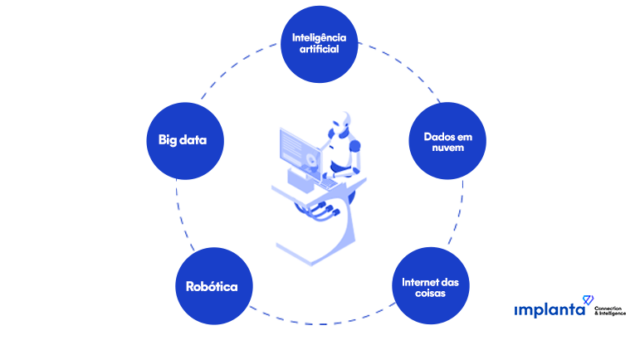
1. Artificial Intelligence
Common in various integration tools within industry, artificial intelligence is a relatively new advancement. However, it ensures greater autonomy and accuracy in industry decision-making.
Artificial intelligence was designed to enhance the success rates of specific decisions by perceiving the environment and scenarios presented to it.
Moreover, it is also a primary tool in terms of machine autonomy and generating insights from compiled data.
2. Big data
As we've seen before, the operations of an industry and the entire process from production to the end consumer generate a vast amount of data that is no longer isolated from the production process.
These large volumes of data are what we currently refer to as big data , and without them, many of the facilitating tools we have today would not exist.
Big data also serves as a significant ally to artificial intelligence technologies. Proper management of big data is essential for industries.
3. Cloud data
The large volume of data produced nowadays also requires ways to facilitate handling them.
This is where technologies that enable cloud data storage come into play, reducing costs for the industry and streamlining the workflow from an informational perspective.
4. Robotics
A term already familiar in the industry, robotics needs to be highlighted beyond the automation of the production system.
As a result, there are increasingly more innovations emerging in the market in this area that serve as the foundation for industrial work. This includes smarter machines that identify production errors and other information that streamline the production cycle.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
The advent of the internet has created a revolution that allows geographical boundaries to be broken, unprecedented communication, and the optimization of various processes.
Moreover, the environment we live in and the elements around us form a giant network that is increasingly interconnected with each other and with the internet.
The philosophy behind the Internet of Things shows us that we are moving towards an increasingly connected world. For industries, this means integrating processes and partners and seeing their products as part of this vast network.
Industry 4.0 and consumer data
The advent of Industry 4.0 also brings a change in how products are consumed, which affects industry production planning.
We know that the flow of data, and consequently information, predominantly travels from consumers to producers.
In other words, it is from consumers that a greater amount of data can be obtained regarding the products sold, their overall performance, which products have potential for sales growth, among other insights.
Armed with this data, the concept of selling products for a specific purpose that merely satisfies a consumer's particular need has evolved.
Nowadays, products extend beyond mere utility and are focused on enhancing customer experience, expanding the concept of a product to not only meet basic needs but also create new services based on these insights.
This shift towards personalization of products and services according to consumer profiles and needs is a significant outcome.
The primary thrust of Industry 4.0 is to enable industries to make intelligent business decisions based on data collected through various tools.
Thus, we can conclude that data forms the foundation of the new industrial revolution, and industries must adapt to these new formats.
Industries are increasingly moving towards production focused on new technologies and the insights these tools can provide. Therefore, knowing how to manage this data correctly will prepare your industry to adapt its strategies and stay ahead.
Looking for tools that can transform your production and provide you with highly accurate real-time data? Count on Implanta! Talk to one of our specialists and discover how to improve your production planning.






