Effective production planning and sales campaigns are crucial elements for a product's success and its market sales.
However, it’s not very beneficial to create strong campaigns and sell well if the product is not distributed efficiently. The logistics process plays a central role in the distribution and sales stages and, therefore, must be meticulously planned.
There are a variety of solutions that make up logistics planning.
For the industry, logistics planning is responsible for optimizing distribution processes and ensuring that products are available to consumers within the specified period. Therefore, good logistics planning can transform relationships with your channels, increase sales, and reduce various costs.
Stay with us to discover how logistics planning improves these and other aspects from the industry's perspective.
An Overview of Logistics Planning
Logistics is a complex process based on a systemic view of a product's lifecycle from production to the final consumer.
The complexity of the logistics process also requires planning that aligns with the previously established objectives.
For the industrial sector, this means adopting methods that create synergy among the stages of production, transportation, and distribution of products.
To achieve this, the manager responsible for logistics planning must conduct an assessment of the industry’s operations. Through analysis, they should seek ways to improve these processes.
Effective logistics planning also provides a competitive advantage for the industry in question. Ensuring product availability at the right time and place can increase profitability and foster customer loyalty.
Today, competitiveness among companies in the production chain depends on building better partnerships and supply chains, rather than on purely individual competition among these companies.
When working on logistics in the industry, there are three fundamental aspects: planning, implementation, and control.
These three stages are essential as the industry's logistics actions require a concise and functional plan, methods of implementation that optimize processes and prevent resource loss, and control mechanisms to evaluate whether the adopted strategies are yielding positive results.
Therefore, developing an appropriate logistics plan to optimize processes is crucial for the success of companies that produce on a large scale, such as in the industrial sector.
The Lack of Adequate Logistics Planning
The absence of proper logistics planning can lead to a range of extra costs. One example is inventory management: excess products in the distributor’s stock generate additional storage expenses.
These inventory costs can increase further if the products suffer from integrity issues or if they are highly perishable, leading to losses.
To track the stages of a product's lifecycle and ensure that there are no stockouts or excess inventory, logistics planning emerges as a tool to optimize this cycle.
But how do you build a concise and effective logistics plan? The guidelines for logistics planning depend on a variety of factors such as the size of the company, its partners and channels, the strategies adopted for selling products, among others.
The plan must also consider both internal and external aspects of the organization to minimize damage in case of errors in the logistics process.
For this reason, logistics planning is based on three essential stages: strategic, tactical, and operational planning. These three elements interact and are crucial for creating functional logistics plans.
3 Foundations for Logistics Planning
As previously discussed, developing an efficient logistics plan involves addressing strategic, implementation, and control aspects.
Therefore, logistics professionals must focus on creating highly efficient supply chains during logistics planning. To achieve this, logistics planning can be structured around three main levels: strategic, tactical, and operational.
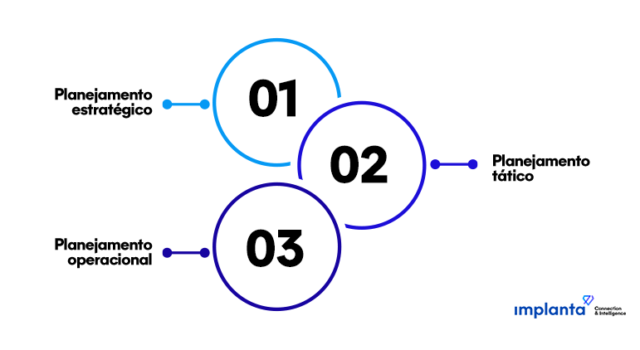
1. Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is tied to the company’s objectives and essentially involves defining long-term logistics strategies and goals.
This set of strategies will align with specific goals: Is the aim to increase market share? Boost productivity? Make product transportation more efficient? These are the questions considered during strategic planning.
At this stage, it is crucial to assess the synergy between departments both within and outside the industry, including partners and distribution and sales channels. It is essential to ensure that there are common strategic business objectives.
During strategic planning, you will diagnose which stages of your logistics process are functioning to meet the industry’s goals. For instance, if the goal is cost reduction, which processes need optimization to reduce logistical costs?
In this specific case, you might examine inventory costs, losses due to inaccurate demand forecasting, and ineffective or unscheduled product transportation.
This stage also includes geographic strategies, such as determining storage and distribution points.
2. Tactical Planning
Building on a more detailed perspective, tactical planning aims to create tactical models to achieve the objectives previously defined in the strategies.
The difference here is that tactical planning will determine how and in which locations each action will impact strategic objectives in specific areas within the industry.
Tactical planning will examine the logistics process with a more technical focus, aimed at solving a problem or improving a procedure.
If the strategic planning has established logistics cost reduction as a strategic goal, tactical planning will define how this will be achieved.
For example, inefficient transportation may result from factors such as the method, timing, and routes used by transporting vehicles. Tactical plans will address these factors.
The role of tactical planning is to put managers of specific areas in front of the problems and develop tactical plans aimed at solving them.
Following the example of a company aiming to reduce costs strategically, tactical planning will involve engaging logistics management roles and creating a plan to reduce logistics costs.
3. Operational Planning
Finally, operational planning is predominantly technical and focuses on the actions specifically outlined in the strategies and tactical plans. As it deals with the operational level, operational planning is the final stage of logistics planning, concentrating on the actual actions.
At this stage, the company will define the operations of each sector, which, in the logistics sector, involves the methods and processes adopted, as well as the people involved in them.
Therefore, operational planning especially focuses on the company’s activities.
With objectives and plans already defined, it is now necessary to create technical models to support these objectives and plans, and this is the role of operational planning.
It is also during this stage that you can define performance indicators. This allows for the monitoring of processes and determining whether they are effective.
Continuing with the example of a company aiming to reduce costs: if the route changes did not bring any optimization in terms of transportation, was the adopted action really effective?
What other indicators do you have to better determine what should be done? Executing actions is as essential as defining plans and objectives, which is why operational planning is so important.
Valuable Insights are Essential for Effective Logistics
We have seen that effective logistics planning requires setting strategic objectives, creating tactical plans, and adopting actions that yield desired results.
However, all stages of logistics planning share a common denominator: the need for accurate information that provides truly valuable insights for the decision-making process.
To create efficient logistics, communication between the channels in the supply chain must be precise and free of disruptions that could hinder operations.
Today, integrating channels is crucial not only for reducing costs but also for generating greater competitiveness and market advantages. Thus, using integration software that allows for data sharing is an essential part of high-quality logistics planning.
Having visibility into the distribution process, obtaining sell-out data directly from point-of-sale locations, tracking product batches, and many other aspects are key elements in developing concise strategies that deliver real results for the industry.
Obtaining accurate data ensures that your decision-making and planning processes are on the right track, leading to growth for the industry and its channels in the supply chain.






